E-Burette Product Guide
- August 10, 2022
- ENQUIRE NOW

What is a Burette?
Burette is an essential laboratory instrument, commonly used in the titration process for quantitative analysis in many industrial chemical tests where solutions of known concentration are used to find the concentration of unknown solutions.
Types of Burette
There are three types of burette:
1. Volumetric Burette
A volumetric burette is made of glass or plastic material, with a volume scale printed on the burette wall. It has a stopcock at the end of the instrument and a valve to control the flow of liquid. The barrel of a stopcock is made of glass or plastic. Burettes are usually fixed with a clamp in an iron stand. Normally, volumetric burette can be classified as:
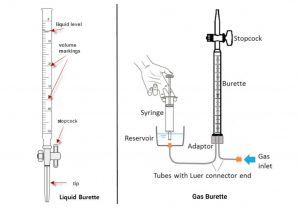
• Liquid burette
• Gas burette
On a liquid burette, it has a long graduated glass tube with a stopcock at the bottom to control the flow of liquid. Gravity causes fluid to flow when the valve is opened. The exact amount of liquid can be determined by reading the volume marked on the glass tube.
In a gas burette, the stopcock is given at the upper side of the burette. The tube of the burette is filled with a fluid, such as water, mercury or other kinds of liquid and is attached to a reservoir of fluid at the bottom of the tube. The gas is collected by displacing the fluid from the burette and the volume of the gas is measured by the volume of the displaced fluid.
2. Piston or Digital Burette
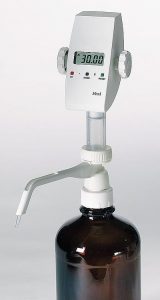
A piston or digital burette is based on a syringe design wherein the barrel and plunger can be made of glass or plastic. For alkali solutions, the barrel and plunger may be made of polyethylene or another resistant plastic material. The barrel is placed in a fixed position and the plunger is moved incrementally by rotating the wheel by hand or by means of a step motor.
The volume is shown on a digital display given at the top of the burette. A high-precision syringe can be used to deliver a very precise amount of liquid. A motorized digital burette can be controlled by a computer.
3. Electronic Burette

The Electronic Burette or E-Burette has an electronic display, electronic control panel and motor controlled piston movements that eliminate all problems of the digital burette which dispense manually. The accuracy of electronic burette is higher than a digital burette due to motor controlled dispensing. This motorized system eliminates human errors in the titration/dispensing process, making the titration more precise.
Technical Specifications of Burette
An Electronic Burette comes in different sizes and the most popular volume ranges are 10ml, 25ml and 50ml in capacity. The technical specification of these burettes are listed below along with their permissible error limits as specified in the DIN EN ISO 8655-3.
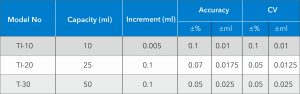
Components of a Burette

• Components of Volumetric Burette:
Volumetric or glass burette consists of a graduated glass tube with a stopcock at one end. The precise liquid dispensed can be determined by volume marking given on the glass tube surface. A Tip is given at the other end of the glass burette which is used to dispense liquid precisely. The Stopcock helps to control the flow of liquid by rotating it clockwise or anti-clockwise.
• Components of Electronic Burette:
E-Burette is an electronic device that delivers accurate and convenient titration while reducing the risk of accidental chemical contact. It includes some advanced components that reduce manual operation with high work efficiency. Some major components of E-burette are:
Recirculation Valve
It prevents the loss of reagents during purging by re-directing them into the mounted bottle.
Delivery Tube
Delivery tube provides the facility to deliver the reagent beyond the reservoir.
Inspection Window
The transparent acrylic window can be replaced with an amber colored window for the use of chemicals. These chemicals such as iodine, potassium permanganate and silver nitrate solutions are sensitive and can react in light. To protect these chemicals from such reactions, an amber-colored window is used that can be easily changed.
Delivery nozzle
Delivery nozzle provides a high degree of flexibility in both the horizontal and vertical directions, facilitating easy dispensing according to different laboratory conditions.
TFT Screen
A user-friendly TFT touchscreen guides quick and accurate titrations and displays numeric data up to the second decimal. It is easily operated with Stylus.
Telescopic tube
The telescopic tube is used to draw up the liquid from the reagent bottle to e-burette. It can be adjusted in length according to a variety of bottle sizes.
Adaptor
E-burette comes with different standard sizes of adapter that comfortably fit most laboratory reagent bottles. The standard sizes of adapters are 28mm, 32mm, 38mm, 40mm and 45mm.
Stylus
It is a sleek hand-held instrument like pen used to operate the control panel with ease.
Control Panel
E-Burette comes with a powerful control panel that is used to perform functions like automatically re-fill without changing the reading, perform a zero reset (via. tare). switch the instrument off etc.
Middle Housing
It consists of a piston mechanism inside the burette.
• Components of Digital Burette:
Digital burette is different from e-burette, although many components have the same functionality. Recirculation Valve, Delivery Tube, Inspection Window, Telescopic tube and Adapters have the same functionality as Electronic Burette. The digital burette only has an electrical display but the piston movement is manual which can be operated manually using a wheel.
A digital display allows the user to note the volume of the liquid dispensed out of the burette. This feature eliminates meniscus reading errors. A hand wheel gives you the facility to set the amount of dispensed liquid by rotating it clockwise or anti-clockwise.
Various buttons including ON/OFF button, CLEAR/Selection button and Pause Button are available at upper housing of the digital burette that helps to control the dispensing process.
How to use a Burette?
The main steps to use an Electronic burette are given below:
Connecting the batteries
• Open the battery panel at the back of the control panel.
• Connect the battery connector to the panel wire by inserting the battery connector into the panel, and then close the panel.
• Press the ON/OFF button. The screen will display “Welcome”.





Setting Up
• Adjust the length of telescopic tube according to reservoir bottle length
• Fix the telescopic tube at the bottom of the burette. Fix it from the wider end.
• Choose the correct adapter according to the reservoir bottle and fix it by screwing it in a clockwise direction.
• Mount the instrument on a reservoir bottle by screwing it with gentle hand torque.

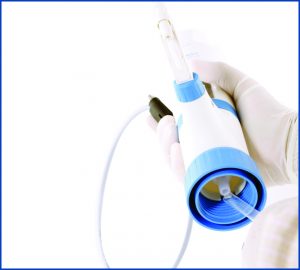


• Connect the cable from the instrument housing to the port at the back of the control panel.
• If the charging is required, insert the charging pin at the back of the control panel and connect the power cord. Battery indicator will show the charging.
• Now E-burette is now ready to be switched on.
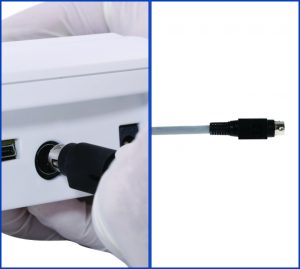




Operating the Instrument
• Switch on the instrument using the ON/OFF switch at the back of the control panel.
• When it boots, the instrument will warn the user to switch the knob to recirculation mode.
• After turning the knob to recirculation mode, click the tick mark on the control panel screen when ready.
• Instrument will reset automatically, now it is ready to use.


Before starting using the digital burette, it is recommended to ensure bubble free dispensing:
• Click the purging mode from the home screen on the control panel.
• The screen on the control panel will warn the user to turn the knob to recirculation mode.
• Turn the knob to recirculation mode and click the tick mark on the control panel screen when ready.
• The digital burette will purge automatically. If the instrument is still not properly purged, repeat the purging process again till no large air bubble is visible below the piston.
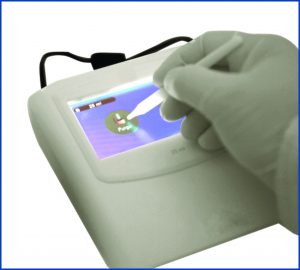


E-burette is commonly used in the titration process to determine the concentration of an unknown solution. Typically, titrant (known solution) is added from a burette to a known volume of analyte (unknown solution) until the reaction is complete. An indicator is used to find the endpoint of the titration.
Once the E-burette is properly setup, follow the steps below to perform the titration process.
• Remove the cap from the discharge tube.
• Click on the titration mode on the home screen. The screen on the control panel will warn the user to turn the knob to titration mode.
• Turn the knob clockwise to set at titration mode and click the tick mark on the screen of the control panel when ready.
• Place the discharge tube orifice against the inner wall of a suitably receiving vessel.
• Now fill the barrel from the titration screen by clicking the fill button. By pressing the stop button, the filling volume can be stopped as and when you need to.
Microlit E-burette offers the free dispensing speeds are provided, including dropwise dispensing that allows the user to get accurate end point of the titration:
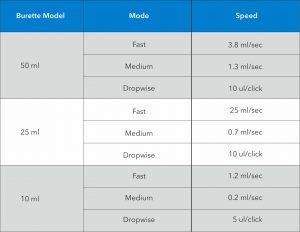
• The user interface is very responsive and the dispensing starts by clicking the appropriate button on the control panel and stops immediately when the touch is removed.
• Press the TARE button to reset to Zero and repeat the process.
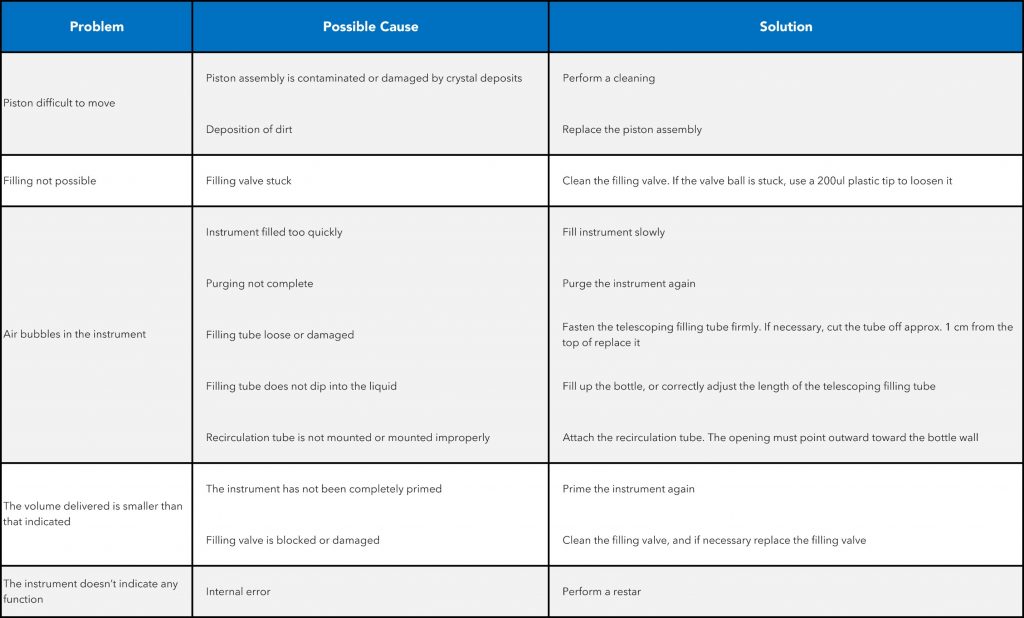
Cleaning, Maintenance and Storage of a Burette
The maintenance of electronic burette is an important routine in any chemical laboratory. Adopting a proper maintenance schedule can reduce the cost of purchasing new equipment. Cleaning the e-burette takes time and practice, otherwise the equipment may deteriorate. Therefore it is necessary to handle the burette carefully while cleaning.
The instrument must be cleaned in the following situations to ensure the correct operations and test results:
1. Immediately, if the piston become harder than normal use
2. Before changing the reagent
3. Prior to long-term storage
4. Prior to dismantling the instrument
5. Regularly when using crystallizing liquids
6. If the liquid has accumulated in the screw cap of the titration tube
Note: The piston cylinder, valves, telescoping filling tube and titration tube may contain the reagent. The necessary safety steps must be taken before cleaning the instrument.
Standard Cleaning of Burette:
Whenever cleaning is required, run the burette under distilled water.
• Fill the barrel completely with distilled water and press the fast dispense button to dispense the water completely.
• Place a suitable receiving vessel below the opening of the discharge tube and rinse the instrument several times by completely filling and emptying it.
• Set the valve to recirculation and rinse the instrument several times by completely filling and emptying it.
• This process can optionally be repeated with a suitable cleaning agent.
• Unscrew the chuck nut by rotating it in anticlockwise direction and pull out the delivery pipe. Clean the delivery pipe with deionized water and assemble it again.
• Next, rinse the burette again with deionized water.
Intensive Cleaning of Burette:
The dispensing cylinder, valve, telescoping filling tube and titrating tube are filled with reagent. For this reason, always perform a standard cleaning before dismantling the instrument.
In order to avoid confusion about the components, do not dismantle more than one instrument at a time. A calibration and any necessary adjustment, must be carried out after dismantling or replacement of a piston/cylinder assembly.
Note: Use rubbing alcohol on a cloth or cotton to clean the external body.
Proper storage of digital burette is as important as cleaning and calibrating the instrument. The digital burette and its all accessories must be stored in a clean, cool and dry place. The storage temperature should be ranging from –20 °C to +50 °C (from –4 °F to 122 °F) is advised with relative humidity between 5% and 95%. Another point to be remembered is that the instrument should be stored in an upright position as recommended by the manufacturer.
Applications of a Burette
Burette is commonly used in the titration process for quantitative analysis in many industrial chemical testing where a solution of known concentration is used to find the concentration of an unknown solution. The process of titration is widely used in various industrial applications listed below:
• Pharmaceutical industry: Purity analysis, Content analysis, Precipitation titration, pH-stat titration
• Wine industry
• Automotive industry
• Food and Beverage industry
• Cosmetic industry
Choosing the right Burette
Choosing the best burette for your application can be a challenging task as the liquid handling market has a variety of options. Before selecting a burette for your lab, it is necessary to consider a few questions:
• Is the burette able to handle your typical volume range of liquid required for titration?
• Does the burette provide different speeds for dispensing for proper titration?
• Is it operated manually or automatically?
• Is the accuracy and precision in reading offered by the burette in accordance with the ISO standards?
The above points ensure correct burette procurement that will work for a long time and improve titration activities in your laboratory.
Microlit’s E-Burette is an advanced laboratory instrument designed keeping ergonomics and smooth operation in mind. The E-burette provides sophisticated features and functionality such as touch screen enabled control panel with graphical user interface (GUI), motor-controlled piston movement and three dispensing speeds to perform accurate titrations.
3 Pre-set Dispensing Speeds

Microlit E-burette offers the 3 calibrated pre-set speeds that allow the user to work at the desired speed while avoiding manual error.
The dropwise dispensing option in the Microlit’s E-Burette allows the user to choose this mode when they are about to reach the end-point of the titration process. The dispense droplet can be as small as 5.0 ul and record a highly accurate end-point of the titration.
TFT Touch Screen Control Panel



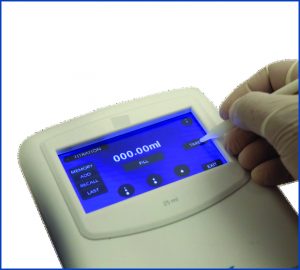
The TFT touchscreen of the control panel helps the user to perform quick, easy and accurate measurements and displays numerical data up to two decimal points. The user needs a Stylus and keeps it pressed against the screen to perform dispensing and lift it to stop. The touchscreen feature also omits any parallax error which normally occurs in glass burettes when it is not viewed from a perpendicular position.
Motor Controlled Piston Movement
Dispensing is done manually in glass and digital burettes leading to inaccurate results. However the Microlit’s E-burette has a motor controlled piston speed that allows laboratory personnel to work efficiently as it does not need to oversee the delivery process at every moment. 3 Pre-set speeds reduce human effort as well as errors which makes it the most efficient lab instrument for liquid handling.
Calibration of a Burette
A gravimetric testing based recalibration of the burette is recommended every 6-12 months depending on the following factors:
• Frequency of use
• Changes in environmental conditions
• The viscosity of the media
For Microlit E-Burette, gravimetric volume testing according to DIN EN ISO 8655-3 should be performed as follows:
• Click the settings icon on the bottom right of the control panel home screen.
• From the settings menu, choose calibration.
• Fill the nominal volume of double-distilled deionized water by clicking the FILL button on the calibration screen of the operating panel.
• Dispense the filled liquid by clicking on the DISPENSE button on the calibration screen of the control panel.
• Measure the dispensed liquid on a balance and enter the value in mg using the provided electronic keyboard. Click the tick mark to proceed. CAL label will start appearing on the top of the screen.
• Repeat the procedure until the nominal volume is achieved on the electronic balance.
Calculation of a Burette Reading
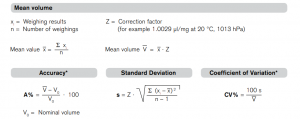
Calculation of accuracy (A %) and coefficient of variation (CV %) are calculated according to the formulas for statistical control.
When is burette calibration required?
In order to maintain the quality of titration results, the burette must be in good condition and properly calibrated. Generally, the interval at which a burette needs to be calibrated depends on several factors:
• Frequency of burette use
• Type of liquid dispensed by the burette
• Long period of non-usage
• Handling and care of burette
• Titration applications that require superior accuracy also demand more frequent calibration
Regulations and standards published by organizations such as the FDA and ASTM International provide minimum requirements to ensure the quality of laboratory testing results. Regulations specify that all laboratory instruments used in sampling & productions including pipette/ burette must be routinely calibrated at suitable intervals.
In the same series, the Clinical and laboratory standards institute (CSLI) has provided the guidelines for pipette/ burette that specifies these instruments must be calibrated every 3 to 6 months. And a minimum of two volumes must be tested with 10 replicas at both nominal and lowest settings.
Establishing an appropriate calibration frequency minimizes the chances of incorrect liquid delivery in the laboratory and ensures traceability, accountability and confidence in the results.
Burette Troubleshooting